Sõnastik (inglise)
Some of the interface text in Estonian and Finnish is machine-translated
| Termin inglise keeles | Termin vene keeles | Termin eesti keeles | Termin soome keeles | Termini tähendus | Foto |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epiphyte | Эпифит | Epifüüt, pealistaim | Epifyytti, Päällyskasvi, Päällyskasvusto | Mostly micro and macroalgae living on other organisms. |
|
| Erosion | (1) Эрозия, размыв (2) Абразия, размыв | Erosioon | Kuluminen, Eroosio | The general process or the group of processes whereby the materials of the Earth's crust are loosened, dissolved, or worn away, and simultaneously moved from one place to another, by natural agencies, which include weathering, solution, corrosion, and transportation, but usually exclude mass wasting; specif. the mechanical destruction of the land and the removal of material (such as soil) by running water (including rainfall), waves and currents, moving ice, or wind. The term is sometimes restricted by excluding transportation (in which case "denudation" is the more general term) or weathering (thus making erosion a dynamic or active process only). |
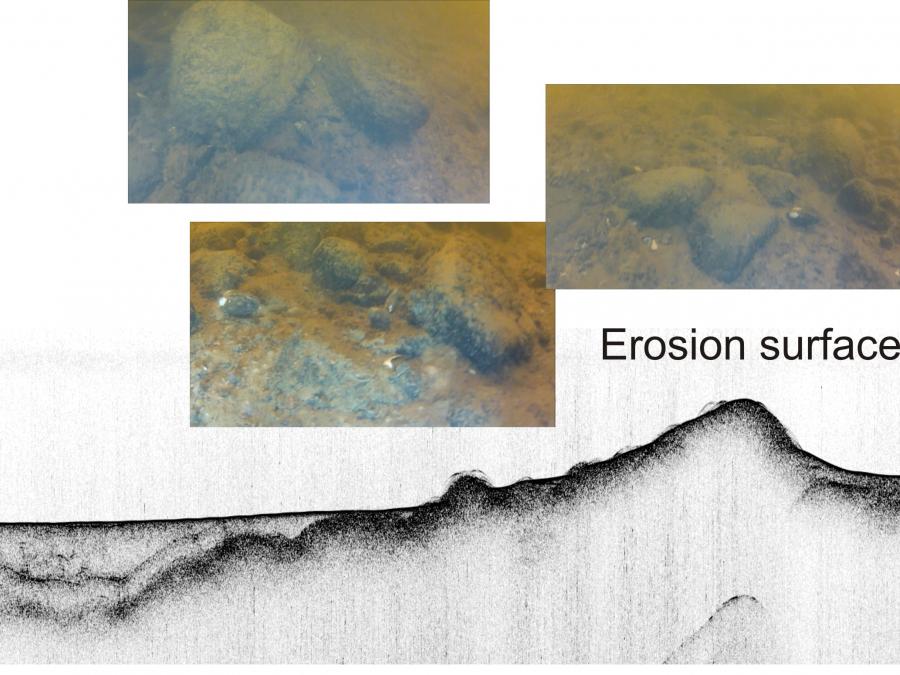
|
| Escarpment | Уступ абразионный | Astang | Jyrkkä rinne, jyrkänne | Elongated and comparatively steep (sometimes vertical) slope separating flat or gently sloping areas. See also Cliff. |
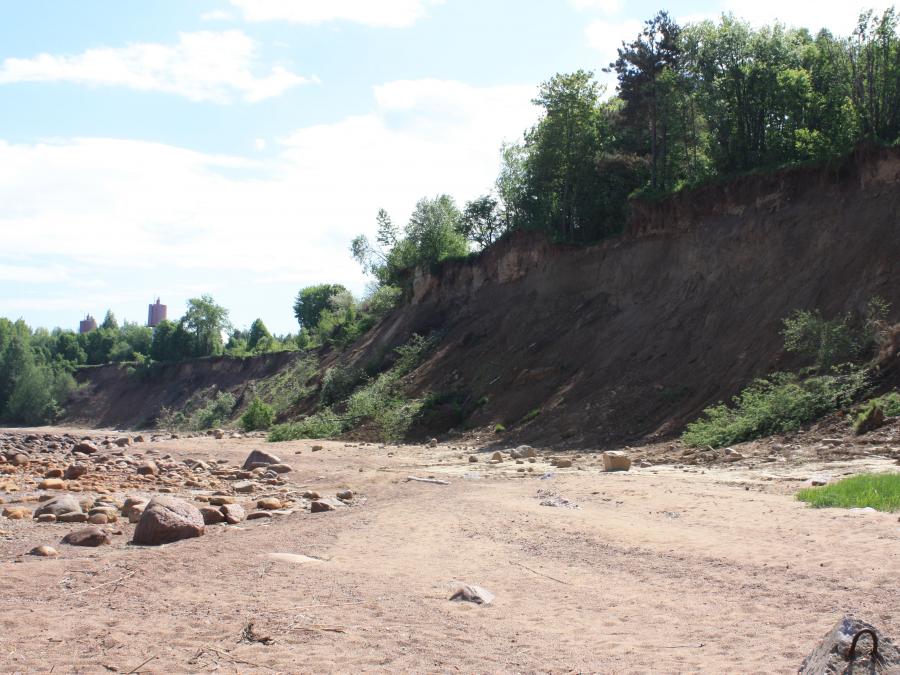

|
| Esker | Эскер, оз | Oos | Harju | An elongate, ridge-shaped sandy-gravelly feature deposited by a glacier. |
|
| Essential fish habitats | Местообитания, важные с рыбохозяйственной точки зрения | Kalade olulised elupaigad | Kalojen olennaiset elinympäristöt | Areas or volumes of water and bottom substrates that provide the most favourable habitats for fish populations to spawn, feed and mature throughout their life cycle, and more specifically, the even more restricted reproduction habitats that have high importance for fish production. Any habitat that is of basic importance to the survival and well-being of a fish population or community, either a habitat used throughout life or for a specific activity such as spawning or feeding. |
|
| Estuary | Эстуарий | Estuaar | Jokisuulahti | (1) A drowned river valley that receives sediment from both landward and seaward sources. Estuary includes salinity gradient from freshwater to marine conditions; (2) Partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea; (3) See more atEstuary. The word "estuary" is derived from the Latin word "aestuarium" meaning tidal inlet of the sea, which in itself is derived from the term "aestus", meaning tide. There have been many definitions proposed to describe an estuary. The most widely accepted definition is: "a semi-enclosed coastal body of water, which has a free connection with the open sea, and within sea water is measurably diluted with freshwater derived from land drainage. However, this definition excludes a number of coastal water bodies such as coastal lagoons and brackish seas. A more comprehensive definition of an estuary is "a semi-enclosed body of water connected to the sea as far as the tidal limit or the salt intrusion limit and receiving freshwater runoff; however the freshwater inflow may not be perennial, the connection to the sea may be closed for part of the year and tidal influence may be negligible". This definition includes classical estuaries as well as fjords, lagoons, river mouths, and tidal creeks. An estuary is a dynamic ecosystem with a connection with the open sea through which the sea water enters with the rhythm of the tides. The sea water entering the estuary is diluted by the fresh water flowing from rivers and streams. The pattern of dilution varies between different estuaries and depends on the volume of fresh water, the tidal range, and the extent of evaporation of the water in the estuary. (4) (biological point of view) – aquatic/marine ecosysytem of transitory type with characteristic peculiarities of bottom morphometry, hydrolocial regime and water balance, those determining presence along its extension of a complex combination of abiotic and biotic factors with expressed periodic and unperiodic variations in values. As a sequence , such a system harbors relatively not many representatives of eurybiotic flora and fauna of mixed origin having especial behavioral, physiological and reproductive adaptations (Komendantov, Orlova 2003). |
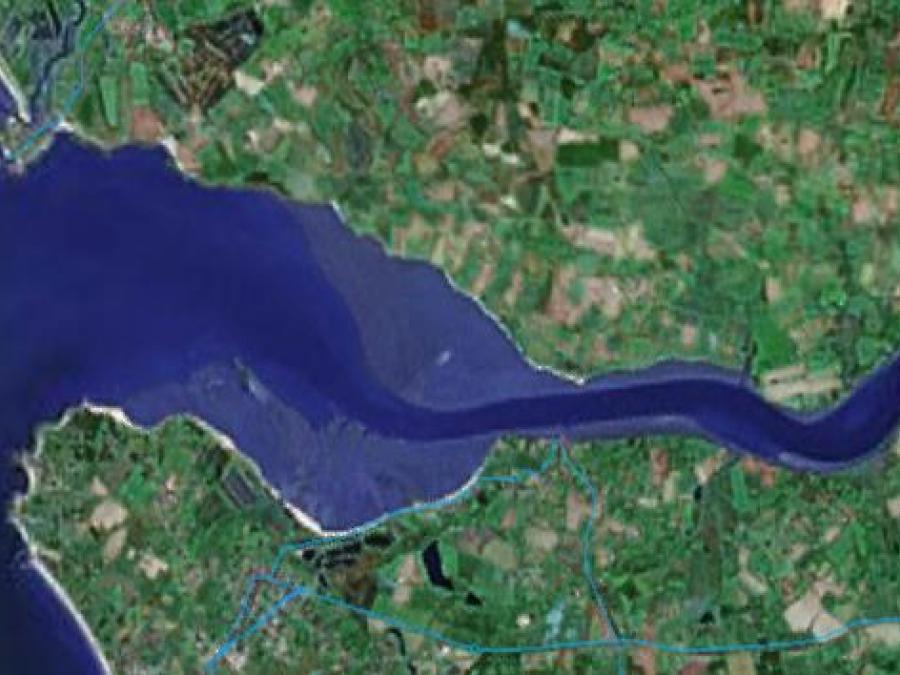

|
| Euphotic zone | Эвфотная зона | Eufootne vöönd | Vesipatsaan valoisa kerros | The upper part of the water column that receives sufficient light to allow plantgrowth. |
|
| Eutrophic | Эвтрофный | Eutroofne | Rehevöitynyt | Of or relating to waters rich in plant nutrients that support high rates of plantgrowth. If the flux of organic matter exceeds the rate at which it can be oxidized (such asoccurs in some enclosed water bodies or basins), the water and sediments may becomeanoxic and dominated by sulfide-reducing bacteria. |
|
| Eutrophication (of waters) | Евтрофирование вод | Eutrofeerumine (vee) | Rehevöityminen | (Russian Federation GOST 17.1.1.01-77)Secondary pollutionIncrease of biological productivity as a consequence of accumulation of nutrients in water. |
|
| Explanatory variable | Независимая переменная | Sõltumatu muutuja | Selittävä muuttuja | A variable which is used in a statistical model to explain or to predict changes in the values of another variable, the latter called the dependent variable. See also predictor variable. |
