Глоссарий (анг)
Some of the interface text in Estonian and Finnish is machine-translated
| Термин на Английском | Термин на Русском | Термин на Эстонском | Термин на Финском | Значение | Фото |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS) | Информационная система по биологии и географии океана (OBIS) | Ookeani biogeograafiline informatsioonisüsteem (OBIS) | OBIS-tietokanta | A database originally created to host biological data collected as part of the Census of Marine Life. In 2009, OBIS was adopted by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, as an activity under its International Oceanographic Data and Information Exchange (IODE) programhttp://www.iobis.org/. |
|
| Oligohaline (Mixo-oligohaline) waters | Олигогалинные (миксо-олигогалинные) воды | Oligohaliinne | Oligohaliini | According to Venice system for thalassic water classification (1959), these are waters with salinity range from 0.5 to 5 ‰. In the Baltic Sea the oligohaline zones, based on biological observations, are divided into α-oligohaline 5-3‰) and beta-oligohaline (3-0.5‰). |
|
| Oligotrophic | Олиготрофный | Oligotroofne, vähetoiteline | Vähäravinteinen | A water body with low level of nutrients and algae, is normally characterized with high transparency. |
|
| Olistostrome | Олистострома | - | Olistostromi | A sedimentary deposit composed of a chaotic mass of heterogeneous material, such as blocks and mud, known as olistoliths, that accumulates as a semifluid body by submarine gravity sliding or slumping of the unconsolidated sediments. |
|
| Opportunistic species | Оппортунистические виды | Oportunistlikud liigid | Opportunistilaji | Opportunistic animal or plant species are adapted to exploit newly available habitats or resources and are typically found in unpredictable, transient, and variable environments. Opportunistic species are most prominent during the early stages of ecological succession, when species that are more competitive in the long run are not very abundant. Opportunistic species have a great ability to alter their growth rate, physiology, or behavior to better suit the environmental conditions with which they are faced. Usually, this opportunistic response is accomplished without changes in the genotype, in which case it is known as phenotypic plasticity. Rather often they are relicts from proceeding geological epochs, e.g. glacial opportunists on the Baltic Sea, such as Saduria entomon – one of the key species for TOPCONS project. |
|
| Oxic sedimentation conditions | Аэробные условия осадконакопления | Aeroobne sete | Hapellinen pohja | High content of oxygen in the near-bottom water and surface bottom sediments. In this case in the Eastern Gulf of Finland surface layer of silty-clayey mud is characterized by light greenish grey or (most frequent) light brown color; preservation of laminas in sediments is usually very bad due to bioturbation. |
|
| Palimpsest | Палимпсестовая | - | Palimpsesti | Sediment that exhibits attributes of a previous depositional environment, but also attributes of the modern environment. |
|
| Peat | Торф | Turvas | Turve | Partially reduced plant or wood material, containing approximately 60 percent carbon and 30 percent oxygen. An intermediate material in the process of coalformation. |
|
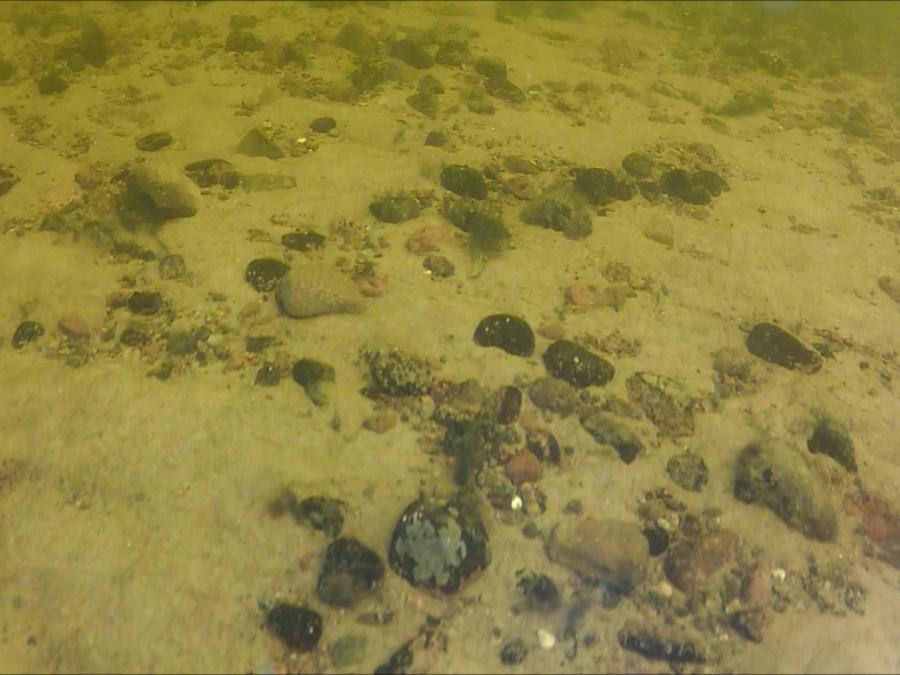
| Pebble | См. Галька | Veeris | Pikkukivi | see Stone, Cobble |

|
| Perennial | Многолетние | Mitmeaastane | Monivuotinen | (1) Animals and plants with life cycle lasting more than one year (see Annual) (2) Present at all seasons of the year. Said of a stream with continual flow. |
