Glossary (eng)
Some of the interface text in Estonian and Finnish is machine-translated
| The term in English | The term in Russian | The term in the Estonian | The term in Finnish | Term article | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geodiversity | Георазнообразие | Geoloogiline mitmekesisus | Geologinen monimuotoisuus, geodiversiteetti | The natural range (diversity) of geological (rocks, minerals, fossils), geomorphological (landforms, processes), and soil (sediment) features. It includes their assemblages, relationships, properties, interpretations, and systems (Gray, 2004). |
|
| Geomorphic feature | Формы рельефа | Geomorfoloogiline vorm | Geomorfologinen muoto | Spatially discrete elements of Earth’s surface (including the ocean floor) attributed to a particular formative process. Examples are dunes, seamounts, atolls, and fjords, formed by wind (or water) currents, volcanism, coral reef growth, and glaciers, respectively. |
|
| Geomorphology | Геоморфология | Geomorfoloogia | Geomorfologia | The scientific study of the shape of Earth’s surface (including the ocean floor) and the formative processes causing them. |
|
| GIS | ГИС | Geoinfosüsteem (lühendatult GIS) | Paikkatietojärjestelmä | Acronym for Geographic Information System - a computer software designed to capture, store, manipulate, statistically analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data. |
|
| Glacial clay | Ледниковые глины | - | Glasiaalisavi | Clay deposited in marine or lacustrine environment during glacial period. Glacial clay consists often of laminated (i.e. varved) units. If exposed on the seafloor there is often a thin layer of coarser materials like sand or/and gravel on top indicating erosion conditions. See: Hard clay. |

|
| Glaciofluvial | Флювиогляциальные, водно-ледниковые | Liustikujõeline | Glasifluviaalinen, ~jäätikköjokisyntyinen | Formed by water that comes from a glacier or ice-sheet. |
|
| Glaciolacustrine | Ледниково-озерные | - | Glasilakustrinen, ~jäätikköjärvisyntyinen | Pertaining to, derived from, or deposited in glacial lakes; especially said of the deposits and landforms composed of suspended material brought by meltwater streams flowing into lakes bordering the glacier, such as deltas, kame deltas, and varved sediments. |
|
| Glo | Гло (в русском языке термин отсутствует) | Rannajärved | Kluuvi | A flad with no further connections to the sea, where the decreasing salinity will lead to a new succession of freshwater plants, unless the glo is overgrown by marsh or land vegetation (The Glossary of Baltic university http://www.balticuniv.uu.se/environmentalscience/index.htm). |
|
| Global warming | Глобальное потепление | Globaalne soojenemine | Ilmaston lämpeneminen | An increase in the near surface temperature of the Earth. Global warming has occurred in the distant past as the result of natural influences, but the term is most often used to refer to the warming predicted to occur as a result of increased emissions of greenhouse gases. Scientists generally agree that the Earth's surface has warmed by about 1 degree Fahrenheit in the past 140 years. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) recently concluded that increased concentrations of greenhouse gases are causing an increase in the Earth's surface temperature and that increased concentrations of sulfate aerosols have led to relative cooling in some regions, generally over and downwind of heavily industrialized areas. See also: Climate change. |
|
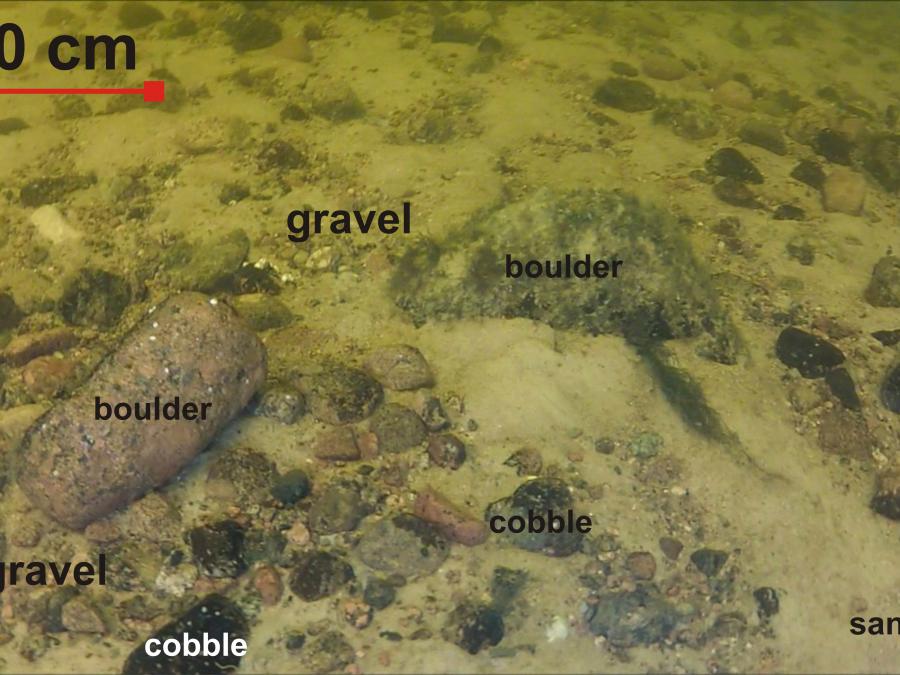
| Gravel | Гравий | Kruus | Sora | Sediment grains larger than 2 mm. Upper limit 60 mm (FIN), 64 mm (EST) or 10 mm (RUS). |

|
